
產(chǎn)品中心
美國強鹿柴油機(jī)維修配件技術(shù)中心
約翰迪爾John Deere柴油機(jī)配件 美國麥克福斯
卡特彼勒柴油發(fā)動機(jī)參數(shù)
沃爾沃發(fā)動機(jī)全系參數(shù)
英國珀金斯原廠配件
珀金斯柴油機(jī)技術(shù)中心
珀金斯發(fā)動機(jī)零件查詢圖冊
日本三菱柴油機(jī)發(fā)電機(jī)配件
德國道依茨 韓國大宇柴油發(fā)動機(jī)配件
康明斯全系列柴油發(fā)動機(jī)
沃爾沃 MTU 原廠配件銷售中心
瑞典沃爾沃遍達(dá)原裝柴油機(jī)配件
康明斯維修技術(shù)中心
卡特彼勒柴油發(fā)動機(jī)原廠配件銷售中心
品牌柴油發(fā)電機(jī)組
康明斯柴油發(fā)動機(jī)配件中心

珀金斯Perkins1306WL-WS用戶手冊
詳細(xì)描述
Perkins Peregrine EDi
Models WL, WN, WQ, and WS
USER’S HANDBOOK
Six cylinder, turbocharged, diesel engines with an
electronic management system for automotive
applications
Publication TPD 1360E, Issue 2.
© Proprietary information of Perkins Engines Company Limited, all rights reserved.
The information is correct at the time of print.
Published in December 2000 by Technical Publications,
Perkins Engines Company Limited, Peterborough PE1 5NA, England
i
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
This publication is written in
Perkins Approved ClearEnglish
This publication is divided into six chapters:
1 General information
2 Engine views
3 Operation instructions
4 Preventive maintenance
5 Engine fluids
6 Fault diagnosis
The following pages contain a detailed table of contents
ii
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()

Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Contents
1 General information
Introduction . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 1
Safety precautions .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 2
How to care for your engine ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 3
Engine preservation ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 4
Parts and service ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 6
POWERPART recommended consumable products .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 6
Service literature . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 8
Training ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 8
Engine identification ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 9
Engine data . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 10
2 Engine views
Introduction . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 11
Location of engine parts .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 11
3 Operation Instructions
How to start the engine ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 13
Starting aid .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 14
How to stop the engine ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 14
Adjustment of engine speed range . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15
Engine operation at idle speed ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15
Running-in ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15
Altitude ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
iii
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
4 Preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance periods . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 17
Schedules ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 18
How to drain the cooling system .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 19
How to fill the cooling system .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 20
How to renew the canister of the coolant filter / inhibitor . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 21
How to check the drive belt . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22
How to renew the drive belt . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22
Fuel pre-filter ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23
How to renew the fuel strainer and the canister of the fuel filter .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23
How to eliminate air from the fuel system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24
How to renew the lubricating oil ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 25
How to renew the canister of the lubricating oil filter ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 26
Air filter ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 27
Restriction indicator . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 27
How to set the valve tip clearances . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 28
5 Engine fluids
Fuel specification . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 31
Lubricating oil specification .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 32
Coolant specification ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 33
6 Fault diagnosis
Problems and possible causes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 35
List of possible causes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 36
iv
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
1
General information
1
Introduction
The Peregrine EDi is a family of engines that have an electronic management system. The engines are
designed for Automotive applications from Perkins Engines Limited, a world leader in the design and
manufacture of high-performance diesel engines.
Perkins approved assembly and quality standards, together with the latest technology, have been applied to
the manufacture of your engine to give you reliable and economic power.
Note: To ensure that you use the relevant information for your specific engine type, refer to "Engine
identification" on page 9.
Danger is indicated in the text by two methods:
Warning! This indicates that there is a possible danger to the person.
Caution: This indicates that there is a possible danger to the engine.
Note: Is used where the information is important, but there is not a danger.
A
W251/1
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
1
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Safety precautions
These safety precautions are important.
You must refer also to the local regulations in the country of use. Some items only apply to specific
applications.
! Only use these engines in the type of application for which they have been designed.
! Do not change the specification of the engine.
! Do not smoke when you put fuel in the tank.
! Clean away fuel which has been spilt. Material which has been contaminated by fuel must be moved to a
safe place.
! Do not put fuel in the tank while the engine runs (unless it is absolutely necessary).
! Do not clean, add lubricating oil, or adjust the engine while it runs (unless you have had the correct training;
even then extreme caution must be used to prevent injury).
! Do not make adjustments that you do not understand.
! Ensure that the engine does not run in a location where it can cause a concentration of toxic emissions.
! Other persons must be kept at a safe distance while the engine or auxiliary equipment is in operation.
! Do not permit loose clothing or long hair near moving parts.
! Keep away from moving parts during engine operation.
Warning! Some moving parts cannot be seen clearly while the engine runs.
! Do not operate the engine if a safety guard has been removed.
! Do not remove the filler cap or any component of the cooling system while the engine is hot and while the
coolant is under pressure, because dangerous hot coolant can be discharged.
! Do not use salt water or any other coolant which can cause corrosion in the closed coolant circuit.
! Do not allow sparks or fire near the batteries (especially when the batteries are on charge) because the
gases from the electrolyte are highly flammable. The battery fluid is dangerous to the skin and especially
to the eyes.
! Disconnect the battery terminals before a repair is made to the electrical system.
! Only one person must control the engine.
! Ensure that the engine is operated only from the control panel or from the operator's position. Discard used
lubricating oil in a safe place to prevent contamination.
! Ensure that the control lever of the transmission drive is in the "out-of-drive" position before the engine is
started.
! The combustible material of some components of the engine (for example certain seals) can become
extremely dangerous if it is burned. Never allow this burnt material to come into contact with the skin or with
the eyes.
! Diesel fuel and lubricating oil (especially used lubricating oil) can damage the skin of certain persons.
Protect your hands with gloves or a special solution to protect the skin.
! Do not wear clothing which is contaminated by lubricating oil. Do not put material which is contaminated
with oil into the pockets of clothing.
! Discard used lubricating oil in accordance with local regulations to prevent contamination.
! Use extreme care if emergency repairs must be made in adverse conditions.
! Always use a safety cage to protect the operator when a component is to be pressure tested in a container
of water. Fit safety wires to secure the plugs which seal the hose connections of a component which is to
be pressure tested.
! Do not allow compressed air to contact your skin. If compressed air enters your skin, obtain medical help
immediately.
Continued
2
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
! Turbochargers operate at high speed and at high temperatures. Keep fingers, tools and debris away from
the inlet and outlet ports of the turbocharger and prevent contact with hot surfaces.
! The fuel injector units of this engine are controlled electronically by a pulse of 110 volts.
! The fuel injector units are actuated by high-pressure engine lubricating oil. Do not remove any component
of the high-pressure system while the engine oil is under pressure, because dangerous oil can be
discharged.
! Fit only genuine Perkins parts.
How to care for your engine
This handbook has been written to assist you to maintain and operate your engine correctly.
To obtain the best performance and the longest life from your engine, you must ensure that the maintenance
operations are done at the intervals indicated in "Preventive maintenance". If the engine works in a very dusty
environment or other adverse conditions, certain maintenance intervals will have to be reduced. Renew the
filter canisters and lubricating oil regularly in order to ensure that the inside of your engine remains clean.
Ensure that all adjustments and repairs are done by personnel who have had the correct training. Perkins
distributors have this type of personnel available. Parts and service can also be obtained from a Perkins
distributor.
The terms "left side" and "right side" apply when the engine is seen from the flywheel end.
Warning! Read the "Safety precautions" on page 2 and remember them. They are given for your protection
and must be applied at all times.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Engine preservation
Introduction
The recommendations indicated below are designed to prevent damage to the engine when it is withdrawn
from service for a prolonged period. Use these procedures after the engine is withdrawn from service. The
instructions for the use of POWERPART products are given on the outside of each container.
Procedure
Caution: The procedure for this engine is different to the procedure for other Perkins engines, because of the
design of the fuel injection units.
1 Completely clean the outside of the engine.
2 Operate the engine until it is warm. Stop the engine and drain the lubricating oil from the sump. Ensure that
the oil gallery of the high-pressure lubrication system is drained.
Caution: If the gallery is not drained, the engine cylinders will be filled with engine lubricating oil when the fuel
injector units are removed.
3 Disconnect the battery.
4 Disconnect the air inlet pipe at the rocker cover. Release the setscrews and remove the rocker cover. Spray
POWERPART Lay-Up 2 around the rocker shaft assembly and into the induction ports in the cylinder head, as
indicated on the container label.
5 Drain the fuel supply gallery, fitted to the cylinder head.
Caution: If the gallery is not drained, the engine cylinders will be filled with fuel when the fuel injector units are
removed.
6 Remove the fuel injector units, see the Workshop Manual, and spray POWERPART Lay-Up 2 for one to two
seconds into each cylinder bore with the piston at bottom dead centre.
7 Slowly turn the crankshaft one revolution and then fit the fuel injector units, complete with new seat washers.
8 Fit the rocker cover and connect the air inlet pipe.
9 Renew the canister of the lubricating oil filter, see "How to renew the canister of the lubricating oil filter" on
page 26.
10 Fill the sump to the full mark on the dipstick with new and clean lubricating oil and add POWERPART Lay-
up 2 to the oil to protect the engine against corrosion. If POWERPART Lay-Up 2 is not available, use a correct
preservative fluid instead of the lubricating oil. If a preservative fluid is used, this must be drained and the
lubricating oil sump must be filled to the correct level with normal lubricating oil at the end of the storage period.
11 Drain the coolant circuit, see "How to drain the cooling system" on page 19. In order to protect the cooling
system against corrosion, fill it with an approved antifreeze mixture because this gives protection against
corrosion.
Caution: If protection against frost is not necessary and a corrosion inhibitor is to be used, it is recommended
that you consult the Technical Service Department, Perkins Engines Company Limited, Peterborough.
12 Connect the battery, eliminate air from the fuel system. Operate the engine for a short period in order to
circulate the lubricating oil and the coolant in the engine. Then correct leakages of fuel, lubricating oil or air.
13 Disconnect the battery. Then put the battery into safe storage in a fully charged condition. Before the
battery is put into storage, protect its terminals against corrosion. POWERPART Lay-Up 3 can be used on the
terminals.
14 Remove the air filter. Then, if necessary, remove the pipe(s) installed between the air filter and the
turbocharger. Seal the air inlet to the turbocharger with waterproof tape.
Continued
4
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
15 Remove the exhaust pipe. Spray POWERPART Lay-Up 2 into the exhaust manifold or the turbocharger.
It is recommended that the spray time for the turbocharger is 50% longer than the spray time for the manifold,
which is indicated on the container label. Seal the manifold or the turbocharger with waterproof tape.
16 Clean the engine breather pipe and seal the end of the pipe.
17 When a preservative fuel is to be used, drain the fuel system and fill it with the preservative fuel.
POWERPART Lay-Up 1 can be added to the normal fuel to change it to a preservative fuel. If preservative fuel
is not used, the system can be completely filled with normal fuel but the fuel must be drained and discarded at
the end of the storage period together with the fuel filter canister.
18 Remove the drive belts and put them into storage.
19 Seal the vent pipe of the fuel tank or the fuel filler cap with waterproof tape.
20 In order to prevent corrosion, spray the engine with POWERPART Lay-Up 3. Do not spray the area inside
the alternator cooling fan.
If the engine protection is done correctly according to the above recommendations, no corrosion damage will
normally occur. Perkins are not responsible for damage which may occur when an engine is in storage after a
period in service.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
5
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Parts and service
If problems occur with your engine or with the components fitted onto it, your Perkins distributor can make the
necessary repairs and will ensure that only the correct parts are fitted and that the work is done correctly.
POWERPART recommended consumable products
Perkins have made available the products recommended below in order to assist in the correct operation,
service and maintenance of your engine and your machine. The instructions for the use of each product are
given on the outside of each container. These products are available from your Perkins distributor.
POWERPART Antifreeze
Protects the cooling system against frost and corrosion. Part number 21825166.
POWERPART Easy Flush
Cleans the cooling system. Part number 21820122.
POWERPART Gasket and flange sealant
To seal flat faces of components where no joint is used. Especially suitable for aluminium components. Part
number 21820518.
POWERPART Gasket remover
An aerosol for the removal of sealants and adhesives. Part number 21820116.
POWERPART Griptite
To improve the grip of worn tools and fasteners. Part number 21820129.
POWERPART Hydraulic threadseal
To retain and seal pipe connections with fine threads. Especially suitable for hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Part number 21820121.
POWERPART Industrial grade super glue
Instant adhesive designed for metals, plastics and rubbers. Part number 21820125.
POWERPART Lay-Up 1
A diesel fuel additive for protection against corrosion. Part number 1772204.
POWERPART Lay-Up 2
Protects the inside of the engine and of other closed systems. Part number 1762811.
POWERPART Lay-Up 3
Protects outside metal parts. Part number 1734115.
POWERPART Metal repair putty
Designed for external repair of metal and plastic. Part number 21820126.
POWERPART Pipe sealant and sealant primer
To retain and seal pipe connections with coarse threads. Pressure systems can be used immediately. Part
number 21820122.
Continued
6
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
POWERPART Radiator stop leak
For the repair of radiator leaks. Part number 21820127.
POWERPART Retainer (high strength)
To retain components that have an interference fit. Part number 21820638.
POWERPART Retainer (oil tolerant)
To retain components that have an interference fit, but is in contact with oil. Part number 21820603.
POWERPART Safety cleaner
General cleaner in an aerosol container. Part number 21820128.
POWERPART Silicone adhesive
An RTV silicone adhesive for application where low pressure tests occur before the adhesive sets. Used for
sealing flange where oil resistance is needed and movement of the joint occurs. Part number 21826038.
POWERPART Silicone RTV sealing and jointing compound
Silicone rubber sealant that prevents leakage through gaps. Part number 1861108.
POWERPART Stud and bearing lock
To provide a heavy duty seal to components that have a light interference fit. Part number 21820119 or
21820120.
POWERPART Threadlock and nutlock
To retain small fasteners where easy removal is necessary. Part number 21820117 or 21820118.
POWERPART Universal jointing compound
Universal jointing compound that seals joints. Part number 1861117.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
7
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Service literature
Workshop manuals, installation drawings and other service publications are available from your Perkins
distributor at a nominal cost.
Training
Local training for the correct operation, service and overhaul of engines is available at certain Perkins
distributors. If special training is necessary, your Perkins distributor can advise you how to obtain it at the
Perkins Customer Training Department, Peterborough, or other main centres.
8
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Engine identification
The Peregrine EDi engines consist of a range of six cylinder in-line engines that are turbocharged /intercooled.
The engines have an electronic management system.
In this handbook, the different engine types are indicated by their code letters, which are the first two letters of
the engine number as indicated below:
Capacity
Code letters
Aspiration system
Litre
7,6
in3
466
531
466
531
WL
WN
WQ
WS
Turbocharged / intercooled
Turbocharged / intercooled
Turbocharged / intercooled
Turbocharged / intercooled
8,6
7,6
8,6
The engine number is stamped on the left side of the cylinder block (A1), behind the high pressure pump.
An example of an engine number is WP1296N123456.
The components of the engine number are as follows:
WP1296N123456
WP = Type code letters
1296 = Build list number
N= Built in the USA
123456 = Engine serial number
Note: If parts, service or information are necessary for your engine, the complete engine number must be
given to a Perkins distributor.
1
A
W002
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
9
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
1
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Engine data
Number of cylinders... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..6
Cylinder arrangement ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. In line
Cycle.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Four stroke
Induction system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Turbocharged/intercooled
Combustion system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Direct injection
Nominal bore:
- WL ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 109,2 mm (4.301 in)
- WN, WQ, and WS ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 116,6 mm (4.590 in)
Stroke:
- WQ .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 118,9 mm (4.681 in)
- WL, WN and WS.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 135,9 mm (5.350 in)
Compression ratio:
- WL and WQ . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..16.5:1
- WN and WS up to 205 kw (275 bhp) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..16.9:1
- WN and WS over 205 kw (275 bhp) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..17.2:1
Cubic capacity:
- WL, and WQ ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 7,64 litres (466.4 in3)
- WN, and WS ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 8,71 litres (531.0 in3)
Firing order. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4
Valve tip clearances (cold):
- Inlet and exhaust . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,64 mm (0.025 in)
Lubricating oil pressure (minimum):
- Idle... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 103 kPa (15 lbf/in ) 1,06 kgf/cm2
- Maximum engine speed and normal engine temperature ... ... 276/483 kPa (40/70 lbf/in ) 2,81/4,92 kgf/cm2
Capacity of a typical lubricating oil sump (1):
2
2
- Without filter canister ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 22,7 litres (39.9 UK pints) 24 US quarts
- With filter canister ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 28,3 litres (49.9 UK pints) 28 US quarts
Typical coolant capacity (engine only)... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 12,8 litres (22.5 UK pints) 13,5 US quarts
Direction of rotation ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Clockwise from the front
(1) The capacity of the sump may vary according to the application. Fill to the "Full" mark on the dipstick. Do not exceed the "Full" mark.
10
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
2
Engine views
2
Introduction
Perkins engines are built for specific applications and the views which follow do not necessarily match your
engine specification.
Location of engine parts
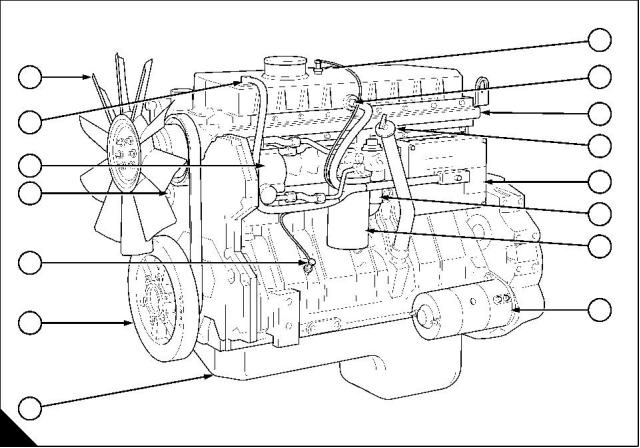
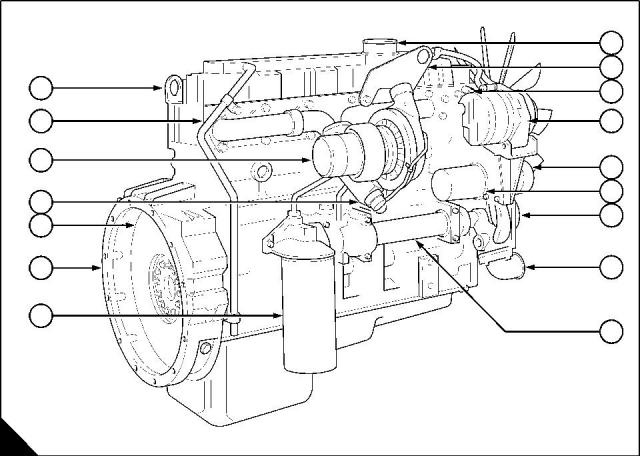
Front and left side view
1 Fan
8 Sensor for the inlet manifold air temperature
2 Wiring harness to the sensor for injection control 9 Electrical connector for the injector units
pressure
10 Supply manifold
3 Sensor for engine oil temperature
11 Lubricating oil filler and dipstick
4 Camshaft position sensor
12 Engine control module
5 Sensor for engine oil pressure
13 Fuel strainer
6 Crankshaft damper
14 Canister for the fuel filter
7 Sump for the engine lubricating oil
15 Starter motor
8
9
1
2
10
11
3
4
12
13
14
5
6
15
7
A
W251/2
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
11
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
2
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Rear and right side view
16 Rear lift bracket
17 Engine breather pipe
18 Turbocharger
24 Front lift bracket
25 Coolant temperature sensor
26 Alternator
19 Wastegate
27 Tensioner for the drive belt
28 Canister for the coolant filter / inhibitor
29 Coolant pump
20 Flywheel
21 Flywheel housing
22 Canister for the lubricating oil filter
23 Air inlet connection
30 Coolant inlet connection
31 Lubricating oil cooler
23
24
25
16
17
26
18
27
28
29
19
20
21
22
30
31
A
PW250
12
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
3
Operation Instructions
3
How to start the engine
Temperature of 15 °C (60 °F) to -20 °C (-4 °F)
Several factors affect engine start, for example:
! The power of the batteries
! The performance of the starter motor
! The viscosity of the lubricating oil
! The installation of a cold start system
The engine will start without a cold starting aid at temperatures as low as -20 °C (-4 °F). In conditions where
the temperature is lower than this, an ether start system may be necessary.
Before the engine is started the operator should understand fully the reason for the controls and their use.
Before the engine is started:
! Check that there is sufficient coolant and, if necessary, add the correct coolant, see Chapter 4, Preventive
maintenance.
! Check that there is sufficient lubricating oil in the sump and, if necessary, add lubricating oil. See Chapter
4, Preventive maintenance. Ensure that the lubricating oil is of the correct grade for the ambient conditions.
! Fill the fuel tank with fuel of the correct specification, see Chapter 5, Engine fluids.
! Check the air filter and its connections.
! Ensure that all of the electrical connections are tight.
Notes:
! See Chapter 5, Engine fluids for the correct engine fluids.
! The procedures to start the engine may vary according to the application. If possible, consult the User's
Handbook for the application.
1 Apply the hand brake, if the application is fitted with one. Ensure that the transmission is in the out-of-drive
position. Ensure that the engine speed control is in the minimum speed position.
2 Turn the start key to the "ON" position.
Note: Do not operate the engine speed control during engine start, the management system controls the
supply of fuel, and it will ignore signals from the speed control until the engine starts.
3 Turn the start key further to engage the starter motor. If the application has a start button, press and hold
the button.
4 Release the start key (or the button) as soon as the engine starts. The start key will return to the "ON"
position.
Caution: If the engine does not start within 30 seconds, release the start key and wait two to three minutes to
allow the starter motor to cool. If after three tries the engine does not start, turn the key to the "OFF" position.
Continued
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
13
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
![]()
3
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
5 Locate and correct the problem. Always ensure that the engine and starter motor are stationary before the
starter motor is engaged again.
2
2
When the engine starts, check that the lubricating oil pressure exceeds 138 kPa (20 lbs/in ) 1,4 kgf/cm within
the first 10 seconds, see "Engine data" on page 10 for the correct lubricating oil pressure. If a gauge is not
fitted, check that the warning light for low oil pressure is extinguished. If this does not occur, stop the engine
and find and correct the fault. Allow the engine to warm at approximately 1000 rev/min for three to five minutes
before load is applied.
Starting aid
The engine electronics system provides cold start ability down to -20 °C (-4 °F). If it is necessary to start the
engine at an ambient temperature less than this, the customer must provide a suitable cold start system.
How to stop the engine
Turn the engine start key to the "OFF" position.
It is recommended that the engine is operated at idle speed for three to five minutes before the engine is
stopped. This will allow the lubricating oil and the coolant to carry the heat away from large ferrous
components.
14
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
3
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Adjustment of engine speed range
The idle or maximum speed settings cannot be changed by the engine operator.
Engine operation at idle speed
Do not operate the engine for long periods at idle speed as this could have an adverse affect on the engine
performance or damage the engine.
Running-in
A gradual running-in of a new engine is not necessary. Prolonged operation at light loads during the early life
of the engine is not recommended.
Maximum load can be applied to a new engine as soon as the engine is put into service and the coolant
temperature has reached a minimum of 76 °C (170 °F).
! Do not operate the engine at high speeds without a load
! Do not overload the engine.
Altitude
The engine management system will automatically compensate for altitude.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
15
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
This page is intentionally blank
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
4
Preventive maintenance
4
Preventive maintenance periods
These preventive maintenance periods apply to average conditions of operation. Check the periods given by
the manufacturer of the equipment in which the engine is installed. Use the periods that are shortest. When
the operation of the engine must conform to the local regulations these periods and procedures may need to
be adapted to ensure correct operation of the engine.
It is good preventive maintenance to check for leakage and loose fasteners at each service.
These maintenance periods apply only to engines that are operated with fuel and lubricating oil which conform
to the specifications given in this handbook.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
17
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Schedules
The schedules which follow must be applied at the interval (Km, miles or months) which occur first.
A
B
C
D
Every day or every 8 hours
E
F
Every 193,100 Km (120 000 miles)
Every 290,000 to 322,000 Km (180 000 to 200 000 miles)
Annually
Every 19,300 Km (12 000 miles) or 6 months
Every 38,600 Km (24 000 miles) or 12 months
Every 161,000 Km (96 250 miles) or 24 months
G
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Operation
!
!
Check the amount of coolant
Check the intercooler and the coolant radiator for debris
!
!
Renew the canister of the coolant filter (3)
Renew the coolant (4)
!
Check the condition of the drive belt
!
Drain water from the fuel pre-filter (1)
!
Renew the canister of the fuel filter and renew the fuel strainer
!
!
Check the amount of lubricating oil in the sump
Check the lubricating oil pressure at the gauge (1)
!
!
!
Renew the engine lubricating oil (5)
Renew the canister of the lubricating oil filter
Clean or renew the air filter element (or earlier if in extremely dusty conditions)
Ensure that the valve tip clearances of the engine are checked and, if necessary,
adjusted (2)
!
Ensure that the turbocharger impeller and the turbocharger compressor casing are
cleaned (2)
!
!
Ensure that the alternator, the starter motor, and the turbocharger are checked
!
!
Inspect the thermostat (2)
Inspect the electrical system (2)
(1) If one is fitted.
(2) By a person who has had the correct training.
(3) Also if the coolant system has been drained.
(4) The system should be flushed and a new canister fitted.
(5) The oil change interval will change with the sulphur content of the fuel (see the table below and "Fuel specification" on page 31).
The interval to change the canister of the lubricating oil filter is not affected.
Fuel sulphur content (%)
Oil change interval
Normal
<0.5
0.5 to 1.0
>1.0
75% of normal
50% of normal
18
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()

4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
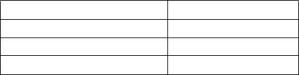
How to drain the cooling system
Warning! Do not drain the coolant while the engine is still hot and the system is under pressure because
dangerous hot coolant can be discharged.
1 Ensure that the machine is on level ground.
2 Remove the filler cap of the cooling system.
3 Place a container of at least 38,65 litres (58.5 UK pints) capacity beneath the drain plug (A1).
4 Remove the drain plug (A1) from the side of the cylinder block (below the rear of the high-pressure pump)
and the drain plug (B1) from the lubricating oil cooler in order to drain the engine. Ensure that the drain holes
are not restricted.
5 Open the tap or remove the drain plug at the bottom of the radiator in order to drain the radiator. If the radiator
does not have a tap or drain plug, disconnect the hose at the bottom of the radiator.
6 Flush the system with POWERPART Easy Flush.
7 Fit the drain plugs and the filler cap. Close the radiator tap or connect the radiator hose.
8 Renew the canister, part number 26550001, of the coolant filter.
Cautions:
! The canister contains a corrosion inhibitor which is circulated around the cooling system as the coolant
passes through the canister. It is important that only the genuine correct Perkins canister is used.
! Discard the used coolant in a safe place and in accordance with local regulations.
1
1
A
B
W005
W006
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
19
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
How to fill the cooling system
Caution: See "Coolant specification" on page 33 for details of the correct coolant to be used in the cooling
system. If coolant is added to the system during service, it must consist of the same original mixture as used
to fill the system. The engine must be allowed to cool before coolant is added.
Warning! Do not remove the filler cap while the engine is still hot and the system is under pressure because
dangerous hot coolant can be discharged.
1 Remove the filler cap of the cooling system.
2 The cooling system must be filled very slowly in order to eliminate air. Fill the cooling system until coolant
reaches the bottom of the filler tube. Fit the filler cap.
3 Start the engine. Allow the engine to operate at a fast idle until the engine reaches its normal temperature
of operation. Stop the engine and allow it to cool.
Remove carefully the filler cap and if necessary add coolant until it reaches the bottom of the filler tube. Fit the
filler cap.
20
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
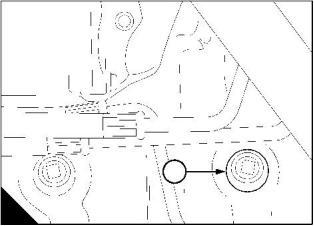
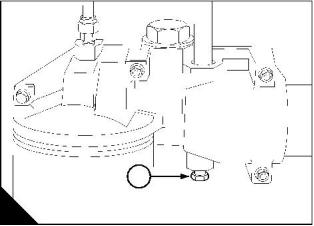
How to renew the canister of the coolant filter / inhibitor
Warning! Do n, ot remove the canister while the engine is still hot and under pressure because dangerous hot
fluid can be discharged.
Caution: The canister contains a corrosion inhibitor which is circulated around the cooling system as the
coolant passes through the canister. It is important that only the genuine correct Perkins canister is used.
1 When the engine has cooled, remove the radiator filler cap to release the system pressure.
Note: When the system pressure is released, valves will close in the filter canister and in the housing for the
canister. This will prevent the loss of coolant when the filter is removed.
2 Thoroughly clean the outside surfaces of the coolant filter assembly.
3 Use a strap wrench or similar tool to loosen the filter canister and remove the canister.
4 Ensure that the threaded adaptor (A2) is secure in the filter head and that the inside of the head is clean.
5 Lubricate lightly the seal (A1) on top of the new canister with clean engine coolant. Fit the new canister to
the filter head and tighten, by hand only. Do not overtighten the canister.
6 Start the engine. Allow the engine to operate at a fast idle until the engine reaches its normal temperature
of operation. Stop the engine and allow it to cool.
7 Remove carefully the filler cap and if necessary add coolant until it reaches the bottom of the filler tube. Fit
the filler cap.
1
2
A
W007
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
21
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
How to check the drive belt
There is no need to check the tension of the belt as the tension is set automatically. The condition of the belt
should be checked. The belt should be renewed if there are cracks in the belt or if the belt is contaminated by
oil or grease.
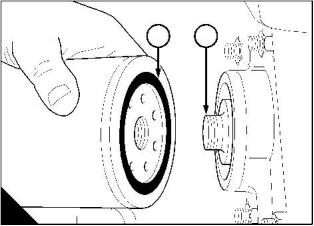
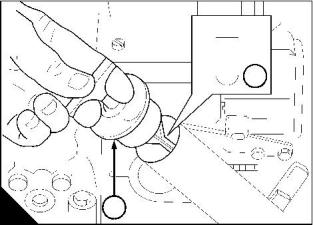
How to renew the drive belt
1 Fit a square headed lever (A3) into the 12,7 mm (0.5 in) hole (A2) in the tensioner assembly (A1). Operate
the lever to release the tension from the belt (A4) and remove the belt. The tensioner will return to its original
position by spring pressure. Remove the lever.
2 With the lever in the tensioner, pull the tensioner outwards. Put the new belt in position around all of the
pulleys. Ensure that the tensioner pulley (A5) is on the outside of the belt. Allow the tensioner to return and
tension the belt. Remove the lever.
1
4
2
5
3
A
W008
22
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
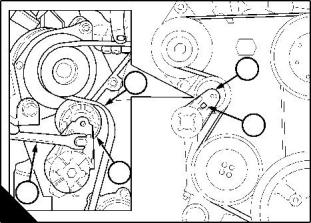
Fuel pre-filter
This will normally be fitted between the fuel tank and the engine. Check the filter bowl for water at regular
intervals and drain as necessary.
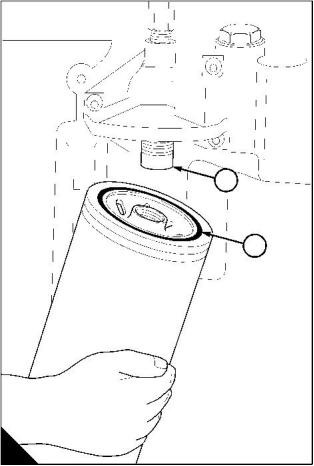
How to renew the fuel strainer and the canister of the fuel filter
The fuel filter assembly has a fuel strainer to remove larger particles from the fuel and a filter canister to remove
the smaller particles. The fuel strainer can be cleaned, but the fuel filter must be renewed.
1 Thoroughly clean the outside surfaces of the fuel filter assembly.
2 Use a strap wrench or similar tool to loosen the filter canister, and remove the canister.
1
3 Use a 29 mm (1 / in) socket spanner to remove the plastic cover (A5) from the fuel strainer. Remove the
8
strainer (A3) and the 'O' ring (A4) from the cover.
4 Fit a new strainer (A3) and a new 'O' ring to the cover and fit the cover to the filter head.
Caution: Ensure that the open end of the new strainer is toward the filter head.
5 Ensure that the threaded adaptor (A1) is secure in the filter head and that the inside of the head is clean.
Lubricate lightly the seal (A2) of the new canister with clean diesel fuel. Fit the new canister to the filter head
1
and tighten the canister by hand until the seal contacts the filter head. Tighten the canister a further / turn by
2
hand only. Do not use a strap wrench.
6 Eliminate the air from the fuel filter, see "How to eliminate air from the fuel system" on page 24.
Caution: It is important that only the genuine Perkins parts are used. The use of wrong parts could damage
the fuel injector units.
3
1
4
2
5
A
W009
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
23
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
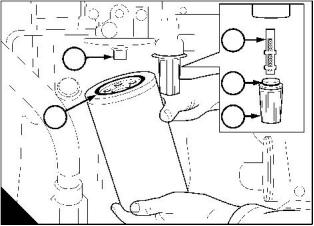
How to eliminate air from the fuel system
If air enters the fuel system, it must be eliminated before the engine can be started.
Air can enter the system if:
! The fuel tank is drained during normal operation.
! The low-pressure fuel pipes are disconnected.
! A part of the low-pressure fuel system leaks during engine operation.
In order to eliminate air from the fuel system, proceed as follows:
1 Loosen the vent plug (A1) on the top of the fuel filter head.
2 Operate the plunger of the fuel priming pump (A2) until fuel, free from air, comes from the filter vent point.
Tighten the vent plug.
3 Turn the start key to the "ON" position.
4 Operate the starter motor for intervals of 15 seconds until the engine starts. If the engine runs correctly for
a short time and then stops or runs roughly, check for air in the fuel system. If there is air in the fuel system,
there is probably a leak in the low pressure system. Turn the start key to the "OFF" position to stop the engine.
Correct the leakage and repeat the procedure.
2
1
A
W011/1
24
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
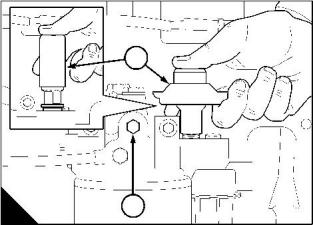
How to renew the lubricating oil
1 Operate the engine until it is warm.
2 Stop the engine.
3 Put a container with a capacity of approximately 30 litres (6.5 UK gallons) 32 US quarts beneath the sump.
Remove the sump drain plug (A1) and its sealing washer and drain the lubricating oil from the sump. Discard
the sealing washer. Fit the drain plug and a new sealing washer and tighten the plug to 68 Nm (50 lbf ft)
6,9 kgf m.
4 Turn the handle on top of the filler cap (B2) counter-clockwise to release the filler cap and dipstick assembly
from the filler tube.
5 Fill the sump to the "FULL" mark on the dipstick (B1) with new and clean lubricating oil of an approved grade,
see "Lubricating oil specification" on page 32.
6 Fit the dipstick and filler cap assembly and turn the handle on the cap clockwise to tighten the filler cap in
the filler tube.
7 Remove the container of used lubricating oil from beneath the engine.
Warning! Discard the used lubricating oil in a safe place and in accordance with local regulations.
8 Start the engine and check for lubricating oil leakage. Stop the engine. After 15 minutes check the oil level
on the dipstick and, if necessary, put more lubricating oil into the sump.
Caution: Do not fill the sump past the "FULL" mark on the dipstick.
Full
Add
1
1
2
A
B
W012
W013
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
25
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
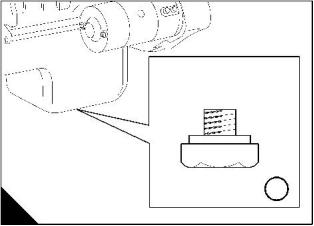
How to renew the canister of the lubricating oil filter
1 Put a tray under the filter to retain spilt lubricating oil.
2 Clean thoroughly the outside surfaces of the filter assembly.
3 Use a strap wrench or similar tool to loosen the filter canister. Remove and discard the canister. Ensure that
the adaptor (A1) is secure in the filter head.
Warning! Discard the used canister and lubricating oil in a safe place and in accordance with local regulations.
4 Clean inside the filter head
5 Lubricate the seal (A2) on top of the canister with clean engine lubricating oil.
6 Fill the new filter canister with clean engine lubricating oil. Fit the new canister and tighten by hand until the
1
3
4
seal contacts the filter head. Tighten the canister a further / to / of a turn by hand only. Do not use a strap
wrench.
2
7 Ensure that there is lubricating oil in the sump.
8 Turn the start key to the "ON" position and start the engine.
Note: The engine will not start and operate until oil pressure is obtained. Oil pressure is indicated when the
warning light is extinguished or by a reading on the gauge.
When the engine starts check for leakage from the filter. Stop the engine. After 15 minutes check the oil level
on the dipstick and, if necessary, put more lubricating oil of an approved grade into the sump.
Caution: Do not fill the sump past the "FULL" mark on the dipstick.
1
2
A
W014
26
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Air filter
Environmental conditions have an important effect on the frequency at which the air filter needs service.
The filter element must be cleaned or renewed according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
Restriction indicator
The restriction indicator for these engines must work at a pressure difference of 635 mm (25 in) of water gauge.
It is fitted on the air filter outlet or between the air filter and the induction manifold.
The restriction indicator should be tested according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
27
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
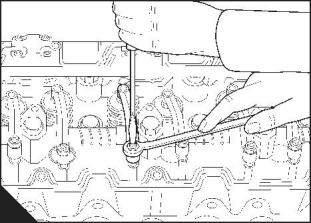
How to set the valve tip clearances
The valve tip clearance is checked with feeler gauges between the top of the valve stem and the rocker lever
(B), with the engine cold. The correct clearance for the inlet valves and the exhaust valves is 0,64 mm
(0.025 in). The valve positions are shown at (A).
The arrangement of the valves for each cylinder in sequence is inlet valve then exhaust valve.
Note: Number 1 cylinder is at the front of the engine.
1 Disconnect the air inlet pipe at the rocker cover /induction manifold.
2 Disconnect the wiring loom for the fuel injector units at the rocker cover connector.
3 Press the four tags that secure the electrical connector for the wiring loom to the rocker cover, and push the
connector into the rocker cover.
4 Release the 13 cap screws that retain the rocker cover and remove the cover.
5 Lift carefully the rocker cover and tilt it away from the exhaust manifold. Ensure that the electrical connector
for the wiring loom is free from the rocker cover then remove the rocker from the engine.
6 Turn the crankshaft in the normal direction of rotation until valve 11 (A) has just opened and valve 12 has
not closed fully. Check / adjust the clearances of valves 1 and 2.
7 Set valves 3 and 4 as indicated above then check /adjust the clearances of valves 9 and 10.
8 Set valves 7 and 8 then check / adjust the clearances of valves 5 and 6.
9 Set valves 1 and 2 then check / adjust the clearances of valves 11 and 12.
10 Set valves 9 and 10 then check / adjust the clearances of valves 3 and 4.
11 Set valves 5 and 6 then check / adjust the clearances of valves 7 and 8.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
A
W015
B
W202/1
Continued
28
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
4
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
12 If necessary, put a new rocker cover / induction manifold gasket in position on the cylinder head.
13 Hold the rocker cover over the engine and push the electrical connector for the wiring loom of the fuel
injector units into its hole in the rocker cover. Ensure that the four tags engage on the rocker cover.
14 Fit the rocker cover, fit and tighten the 13 setscrews that retain the rocker cover and tighten them to 18 Nm
(13 lbf ft) 1,8 kgf m.
15 Connect the wiring loom for the injector units at the rocker cover connector.
16 Connect the air inlet pipe to the rocker cover.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
29
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
This page is intentionally blank
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
5
Engine fluids
5
Fuel specification
To get the correct power and performance from your engine, use good quality fuel. The recommended fuel
specification for Perkins engines is indicated below:
Cetane number
Viscosity
50 minimum
2.0/4.5 centistokes at 40 °C
0,835/0,855 kg/litre
0.2% of mass, maximum
85% at 350 °C
Density
Sulphur
Distillation
Cetane number indicates ignition performance. A fuel with a low cetane number can cause cold start problems
and affect combustion.
Viscosity is the resistance to flow and engine performance can be affected if it is outside the limits.
Density: A lower density reduces engine power, a higher density increases engine power and exhaust smoke.
Sulphur: A high sulphur content (not normally found in Europe, North America or Australasia) can cause
engine wear. Where only high sulphur fuels are available, it is necessary to renew the lubricating oil more
frequently, see "Lubricating oil specification" on page 32.
Distillation: This is an indication of the mixture of different hydrocarbons in the fuel. A high ratio of light-weight
hydrocarbons can affect the combustion characteristics.
Low temperature fuels
Special winter fuels may be available for engine operation at temperatures below 0 °C. These fuels have a
lower viscosity and also limit the wax formation in the fuel at low temperatures. If wax formation occurs, this
could stop the fuel flow through the filter.
If you need advice on adjustments to an engine setting or to the lubricating oil change periods which may be
necessary because of the standard of the available fuel, consult the Technical Service Department of Perkins
International Limited at Peterborough or your nearest Perkins Distributor.
Aviation kerosene fuels
Cautions:
! Do not use aviation kerosene fuel JP4. JP5 and JP8 can be used, but they can affect engine performance
and wear in the fuel injector units could increase. It is recommended that you consult the Technical Service
Department of Perkins International Limited at Peterborough if aviation kerosene fuel is to be used.
! Aviation kerosene fuels are more flammable than diesel fuel and need careful storage and careful
management.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
31
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
![]()
5
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Lubricating oil specification
Lubricating oil to the recommended specification API CG-4, API CH4 or ACEA E3 must always be used in
countries where it is available for purchase. In countries where it is not available, API CF4 or ACEA E2 must
be used.
Caution: The type of lubricating oil to be used may be affected by the quality of the fuel which is available. For
further details see "Fuel specification" on page 31.
Always ensure that the correct viscosity grade of lubricating oil is used for the ambient temperature range in
which the engine will run as shown in the chart (A).
A
0W
5W20
10W30
15W40
20W50
20
30
40
-30
-22
-20
-4
-10
14
0
32
10
50
20
68
30
86
40
50 C
o
o
104 122 F
B
A
Viscosity chart
A = Recommended viscosity grades
B = Ambient temperature
32
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()

5
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
Coolant specification
The quality of the coolant which is used can have a great effect on the efficiency and life of the cooling system.
The recommendations indicated below can help to maintain a good cooling system and to protect it against
frost and / or corrosion.
If the correct procedures are not used, Perkins cannot be held responsible for frost or corrosion damage.
1 If it is possible, use clean soft water in the coolant.
2 If an antifreeze mixture, other than Perkins POWERPART, is used to prevent frost damage, it must have an
ethanediol base (ethylene glycol) with a corrosion inhibitor. It is recommended that the corrosion inhibitor is of
the sodium nitrite / sodium molybdate type. The antifreeze mixture must be an efficient coolant at all ambient
temperatures and it must provide protection against corrosion. It must also have a specification at least as
good as the requirements of either BS6580 or MOD AL39.
Perkins POWERPART antifreeze exceeds the requirements of the above standard.
The quality of the antifreeze coolant must be checked at least once a year, for example, at the beginning of
the cold period. The coolant must be renewed every two years.
The antifreeze mixture must consist of equal quantities of antifreeze and water. Concentrations of more than
50% of antifreeze must not be used because these can affect adversely the performance of the coolant.
3 When frost protection is not necessary, it is still an advantage to use an approved antifreeze mixture
because this gives a protection against corrosion and also raises the boiling point of the coolant. If an approved
antifreeze mixture is not available, add a correct mixture of corrosion inhibitor to the water.
All Peregrine EDi engines are supplied with a coolant filter / conditioner canister. Renew the coolant and the
filter / conditioner canister in accordance with the maintenance "Schedules" on page 18.
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
33
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
This page is intentionally blank
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
6
Fault diagnosis
6
Problems and possible causes
Possible causes
Checks by the workshop
personnel
Problem
Checks by the user
The starter motor turns the engine too slowly
The engine does not start
1, 2, 3, 4
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 37, 38, 42, 43, 44, 66, 67,
15, 17
68, 69
5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
15, 16, 17, 19
The engine is difficult to start
37, 38, 40, 42, 43, 44, 66
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 20, 37, 38, 39, 42, 43, 44, 61,
63, 64, 66, 68, 69
8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 20, 22 37, 38, 39, 40, 43, 66, 69
Not enough power
Misfire
21
11, 13, 15, 17, 18, 19, 22,
23
37, 38, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44,
63, 66
High fuel consumption
37, 38, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44,
61, 63, 66
Black exhaust smoke
11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 22
4, 15, 21, 23
37, 38, 39, 42, 43, 44, 45,
52, 58, 62, 66, 68
Blue or white exhaust smoke
The pressure of the low pressure lubricating oil system
is too low
4, 24, 25, 26
46, 47, 48, 50, 51, 59
37, 40, 42, 44, 46, 52, 53,
60, 66, 68
The engine knocks
The engine runs erratically
Vibration
9, 13, 15, 17, 20, 22, 23
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16, 38, 40, 44, 52, 60, 66, 68,
69
18, 20, 22, 23
38, 39, 40, 44, 52, 54, 66,
68, 69
13, 18, 20, 27, 28
The pressure of the low pressure lubricating oil system
is too high
4, 25
49
11, 13, 15, 19, 27, 29, 30,
32, 65
37, 39, 52, 55, 56, 57, 64,
69
The engine oil temperature is too high
Crankcase pressure
31, 33
39, 42, 44, 45, 52
37, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45,
53, 60
Bad compression
11, 22
The engine starts and stops
10, 11, 12
4, 24, 25, 26
66, 68, 69
The pressure of the high pressure lubricating oil system
is too low
66, 68, 69
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
35
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()

6
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
List of possible causes
1 Battery capacity low.
2 Bad electrical connections.
3 Fault in starter motor.
4 Wrong grade of lubricating oil.
5 Starter motor turns engine too slowly.
6 Fuel tank empty.
7 Spare.
8 Restriction in a fuel pipe.
9 Fault in fuel lift pump.
10 Dirty fuel filter element.
11 Restriction in air induction system.
12 Air in fuel system.
13 Fault in the fuel injector units.
14 Cold start system used incorrectly.
15 Fault in cold start system.
16 Restriction in fuel tank vent.
17 Wrong type or grade of fuel used.
18 Restricted movement of engine speed control.
19 Restriction in exhaust pipe.
20 Engine temperature is too high.
21 Engine temperature is too low.
22 Incorrect valve tip clearances.
23 Too much oil or oil of the wrong type is used in wet type air cleaner, if one is fitted.
24 Not enough lubricating oil in sump.
25 Defective gauge.
26 Dirty lubricating oil filter element.
27 Fan damaged.
28 Fault in engine mounting or flywheel housing.
29 Too much lubricating oil in sump.
30 Restriction in air or water passages of radiator.
31 Restriction in breather pipe.
32 Insufficient coolant in system.
33 Fault in exhauster.
34 Spare.
35 Spare.
36 Spare.
37 Valve timing is incorrect.
38 Bad compression.
39 Cylinder head gasket leaks.
40 Valves are not free.
41 Spare.
42 Worn cylinder bores.
43 Leakage between valves and seats.
44 Piston rings are not free or they are worn or broken.
45 Valve stems and/or guides are worn.
46 Crankshaft bearings are worn or damaged.
36
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
6
Peregrine EDi, Models WL, WN, WQ and WS
47 Lubricating oil pump is worn.
48 Relief valve does not close.
49 Relief valve does not open.
50 Relief valve spring is broken.
51 Fault in suction pipe of lubricating oil pump.
52 Piston is damaged.
53 Piston height is incorrect.
54 Flywheel housing or flywheel is not aligned correctly.
55 Fault in thermostat or thermostat is of an incorrect type.
56 Restriction in coolant passages.
57 Fault in water pump.
58 Valve stem seal is damaged.
59 Restriction in sump strainer.
60 Valve spring is broken.
61 Turbocharger impeller is damaged or dirty.
62 Lubricating oil seal of turbocharger leaks.
63 Induction system leaks.
64 Turbocharger waste-gate does not work correctly, if one is fitted.
65 Drive belt for water pump is loose.
66 Faulty engine management system.
67 Broken drive on the high pressure pump.
68 Faulty injection control system
69 Faulty sensor
User’s Handbook, TPD 1360E, issue 2
37
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
![]()
![]()
